September 21, 2023
Clean-up Recipe: Remove Navigational Pages for Optimal SEO Performance
In this guide, we delve into step-by-step instructions to pinpoint and clean up underperforming navigational pages on your website.
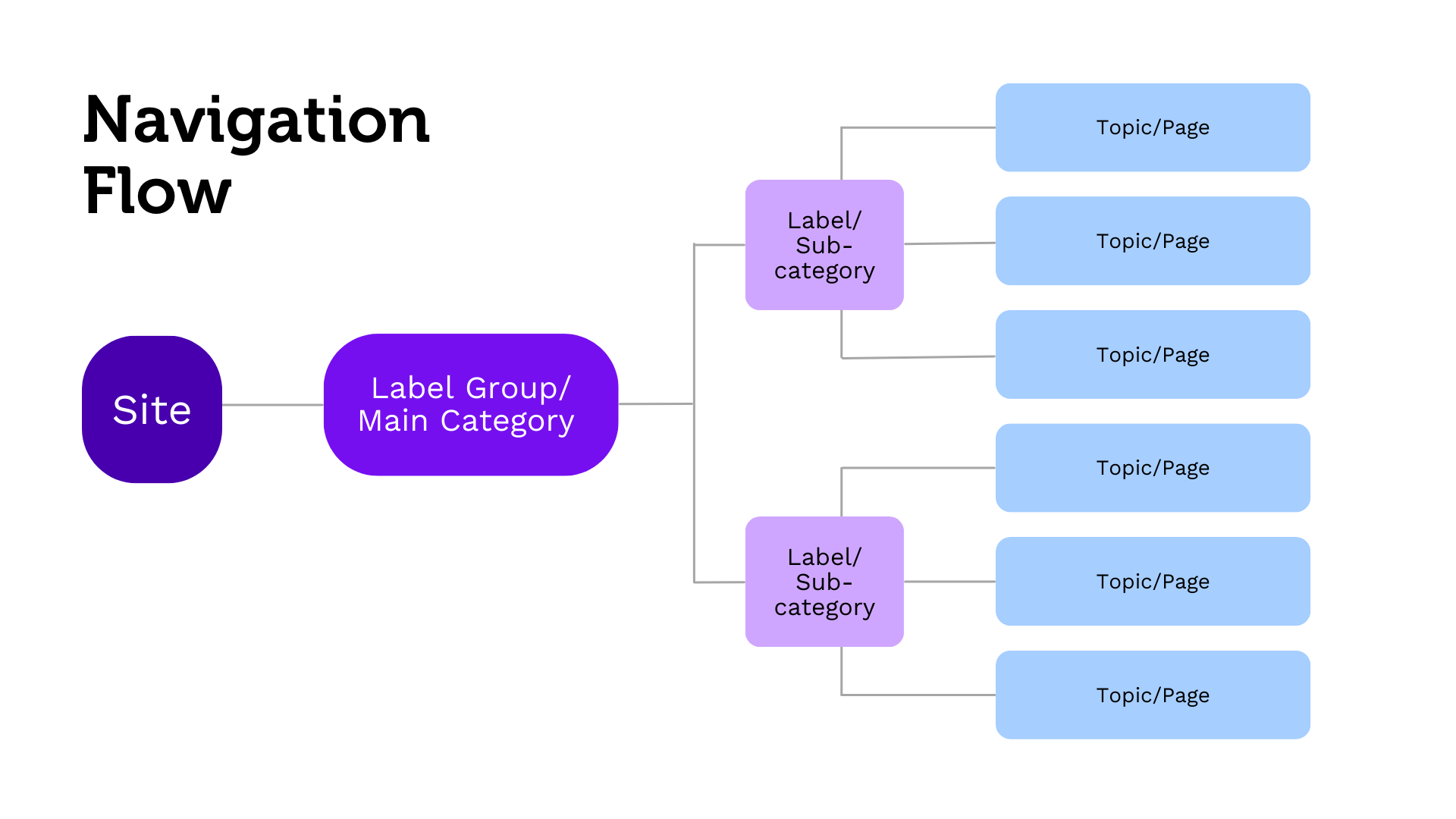
What are navigational pages?
Pages that aren’t generating organic traffic or even ranking, might be underperforming for any number of reasons. For instance, they could be duplicating other pages on the site, they could be targeting insufficient search demand or they might not have well-optimized content.
However, a significant reason for many enterprise sites is that although they have inventory and content and there is search demand, that page is targeting an intent for which it can never get traffic.
Notes: Here, we are not referring to the traditional side navigation (like menus) but the pages targeting navigational search intents.
What does that mean to your SEO?
When users search for a term that includes a brand name, it can be challenging to determine if they’re seeking a product from that brand or a product available on that brand’s website.
Google, through a lot of experimentation, works out what expectations users have for different queries.
Often websites create pages based on a set of internal rules. For instance, perhaps they combine a category and a brand, or a category and some other facet. Unbeknownst to them, they are walking a minefield. Lots of those combinations are not intents for which sites like them can ever rank.
For some queries that mention brands, Google displays a mix of pages from lots of different sites. For other queries, it only shows pages from a single site. (Sometimes it may show queries from the pages of multiple markets of the same site).
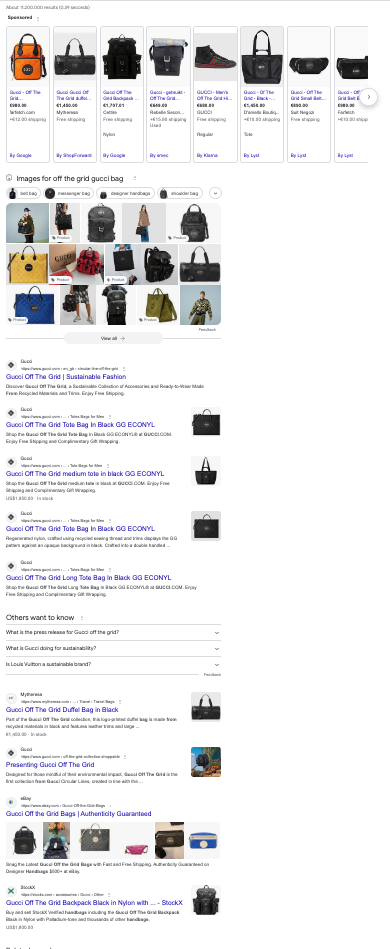
For instance, if you look for off the grid gucci bag in the Netherlands, almost all results on the first page of Google are [gucci.com](<http://gucci.com>). If you’re a multi-brand retailer or marketplace, there is not much point in having a page targeting this intent.
Notes: We use an ingredient called SERP domain diversity to measure how diverse the first page of organic search search results is. If it’s all different sites, the domain diversity is 100% (or 1). If it’s all the same (like in this image), domain diversity is close to 0.
Similar AI lets SEO teams get a view of their pages that matches how search engine users would look at them. We do this by automatically combining different data sources for each of your site pages. Follow the instructions below:
Identifying Navigational Pages Lacking Performance
Step 1: Identifying pages that are underperforming
First, to extract pages on your site that are underperforming, follow this procedure:
- Navigate to Workbench > Site.
- Set Rules for Extraction: Target pages that have received no traffic in the past 12 months and register fewer than 10 impressions.
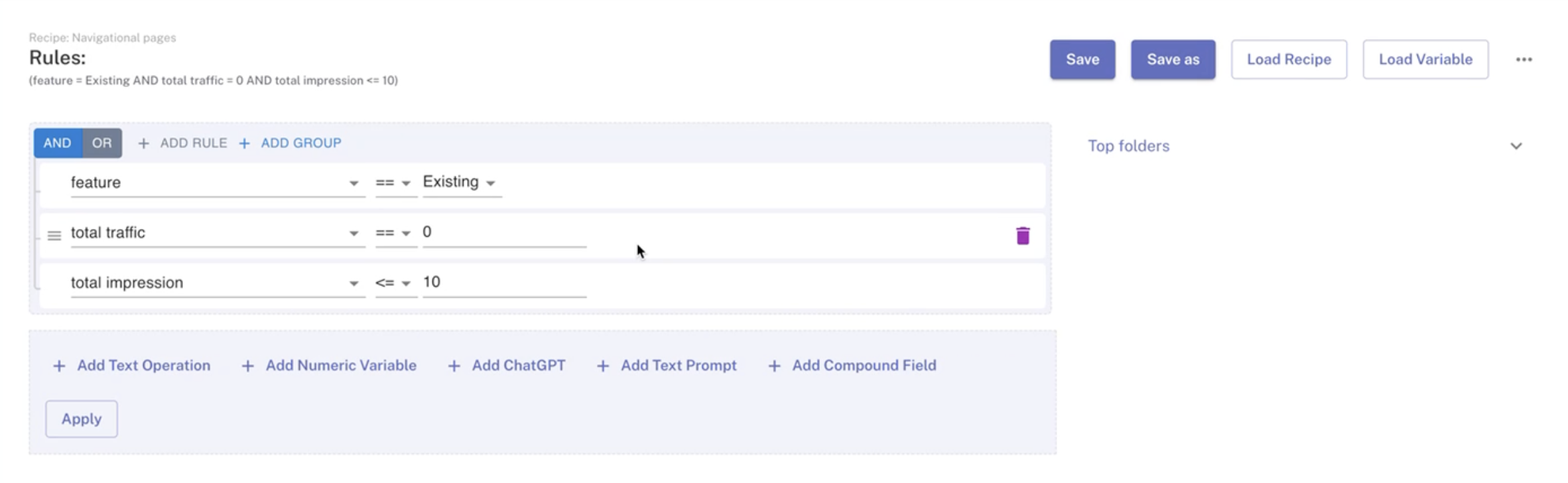
Note: In this recipe, the data is retrieved from the last 12 months, but this range can be adjusted based on your Google Search Console data extraction settings.
- For this particular site, 148,000 pages rank poorly and lack traffic. The list will be displayed in the datatable below after you finish entering the above rules.
Step 2: Pinpointing Navigational Pages
One potential cause is these pages may target search engine result pages (SERPs) that are predominantly navigational. To validate this:
- Enter an additional rule: SERP domain diversity ≤ 0.1
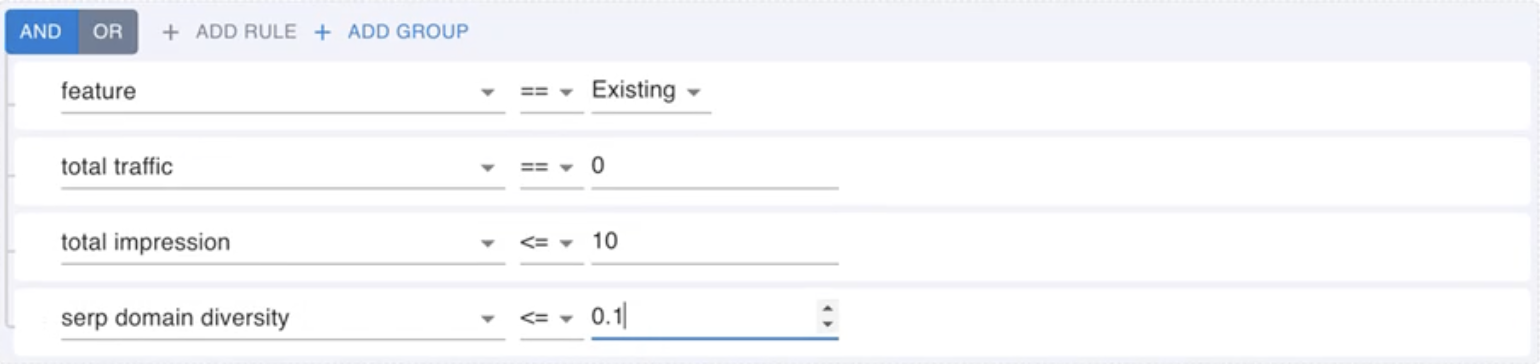
Implementing this set of rules will show us pages targeting SERPs consistently dominated by the same site.
For instance, if your page’s extracted keyword is ‘Nike shoes’ and the majority of top-ranking domains are from nike.com, it’s evident that these pages focus on branded terms.
Step 3: Taking Action on Underperforming Navigational Pages
Depending on your website’s strategy and structure, you can:
410: Let search engines know that this page existed, but doesn’t anymore and will not be in the future. This can be too aggressive if Google changes its mind about what users expect in the future. Some customers have found that Google takes note of this more quickly.No index: Tells search engines not to index the page.301 to parent: Permanently redirects to a parent page. In our example, this is the main page of all category pages.
Once you’ve settled on a suitable action, save it as an opportunity.

What is an opportunity in Similar AI?
An opportunity can include pages that you’d like to consolidate, eliminate, link to, boost links to, create, or to which to add content.
After saving the action, you can see it under the ‘Opportunities’ view. The ‘Opportunities’ view displays potential areas for site optimization to enhance organic traffic and revenue. It allows you to create an action plan detailing what changes to make and on which pages.
You can share an opportunity with clients or team members to show what you plan to do to the site, on which pages, and why.
Once decided upon, click
Publishto implement them on your live site. To view live opportunities, check the ‘Optimisations’ tab and start tracking its impact.
In Conclusion
Understanding the real-time behavior of search engine users is a paramount challenge.
At its core, Similar.ai provides your SEO team with a unique perspective, simulating how search engine users perceive your company’s site. By seamlessly combining multiple data sources, such as matching SERP data to your pages, we present an ‘outside-in’ viewpoint, showing how users search for your pages.
This isn’t just analytics; it’s a roadmap to continuous improvement, allowing you to refine your site in true alignment with user behavior.